
By Allison L. Hurst
Professor, Oregon State University
From the USW Blog
March 18, 2017 – This has been a rough year. After the election, I reposted a few articles on my Facebook wall, as did so many of my friends, about the “working-class vote.” Did the white working-class just elect Trump? I didn’t think so, but I also understood that the world can look very different to a working-class person than it does to a middle-class one. I knew this because I grew up poor, and it is a constant struggle speaking to both sides of my life, my past and my present, my mother and my colleagues. My mother, let me point out, did not vote for Trump. She thinks he’s a jackass. Two of her sisters did, however. I don’t know anyone else in my extended family who voted for him. There were lots of Bernie supporters, not many Clinton supporters, and a whole bunch of abstainers.
A friend of mine from college, someone raised on the less wealthy spectrum of the educated middle class, took issue with even the idea of the “working class.” What was this really? He knew a lot of blue-collar workers, plumbers, builders, who made a lot more money than he or his mother ever did. I gave him the quick sociological explanations — it’s about power, not money, but his question remained with me. Based on power at work, two-thirds of Americans can be classified as “working class” (see Michael Zweig’s excellent The Working-Class Majority). That is a hell of a lot of people. They don’t all think alike. It struck me that sociologists, myself included, have spent untold ink arguing over the distinctions within the middle class (lower-middle, upper-middle, professional-managerial, those with economic capital vs. those with cultural capital, etc.) and where the line is between wherever this middle is and the top, and yet we have spent hardly any time looking within the largest class of them all.
So, I pulled out the General Social Survey (GSS), which has been asking thousands of Americans every year or so all about their lives, political identifications, and voting patterns. I decided to see if there were differences within the working class based on type of working-class job, and not on education, race or income level. Working-class jobs are those with little autonomy and often involving the use of one’s body – to wield a hammer, carry a baby, deliver a package from Amazon, stand all day greeting customers. These jobs are held by a very diverse group of people; there are more people of color in the working class than in the middle or upper class. When I refer to “the working class,” I mean this whole diverse group, not only white male workers.
Let me give you a snapshot of five fractions of the working class: the Builders, the Makers, the Movers, the Clerks, and those who Serve (I call this category “CookCleanCare” to remind myself of the range of work within this fraction). Builders most fit the stereotype of “the working class” (three-quarters are men, most are white, and many of them do wear hard hats at work), but it is only one fraction. A more diverse lot are Makers, including assembly-line workers, tool-and-die makers, sewers, and cabinetmakers. This is the fraction that has seen the largest influx of women in the past few decades, although still mostly male. Movers include a wide array of transport jobs, from UPS drivers to ambulance drivers to long-haul truckers, also mostly men. Most of those in the other two fractions are female. The CookCleanCare group includes those who prepare our food, clean our messes, and care for our children. The Clerks are our growing retail worker category. Back in the day being a clerk was seen as a move up, but today’s clerks are generally poorly paid and even less likely to hold a college degree than CookCleanCare workers (the most educated fraction).
Here are some other interesting differences between the fractions. Builders are the most likely to be living in the same place where they grew up, Makers the least likely. Movers are the most likely to identify themselves as “working class.” Twice as many Builders as Makers think of themselves as “middle class.” Makers, in contrast, are more likely than the others to think of themselves as “lower class.” In terms of income, Builders make the most money, Movers the least. If we looked only at white men in each of the fractions, we would find the most instances of sexism, nativism, and racism among the Makers, perhaps reflecting the fact that this group has seen the biggest changes over the past few decades. But it is important to note that a greater proportion of rich white men and white male managers express racist views than any working-class fraction does.
During the past decade or two, ever since Reagan really, we have been hearing a lot about how “the working class” has turned its back on the Democratic Party. But this is only true if we limit “the working class” to white men without college degrees. If we include the whole of the working class, this claim is simply wrong. According to my analysis of GSS data, there has never been a presidential election in which the majority of the working class voted for the Republican candidate.
If we look at the working class based on broad occupational categories rather than race or education, we get a very different picture from “the working class” that political pundits have been talking about. We don’t yet have GSS data for the 2016 election, but figures from 2012 suggest the value of analyzing working-class voters based on their jobs rather than income or education.
This graph of voting patterns in the 2012 Presidential Election, arrayed by largest supporters of Obama from left to right, shows that while all occupational groups gave Obama a majority, two working-class fractions were at the polar ends of the spectrum. The Professional-Managerial Class fell near the middle.
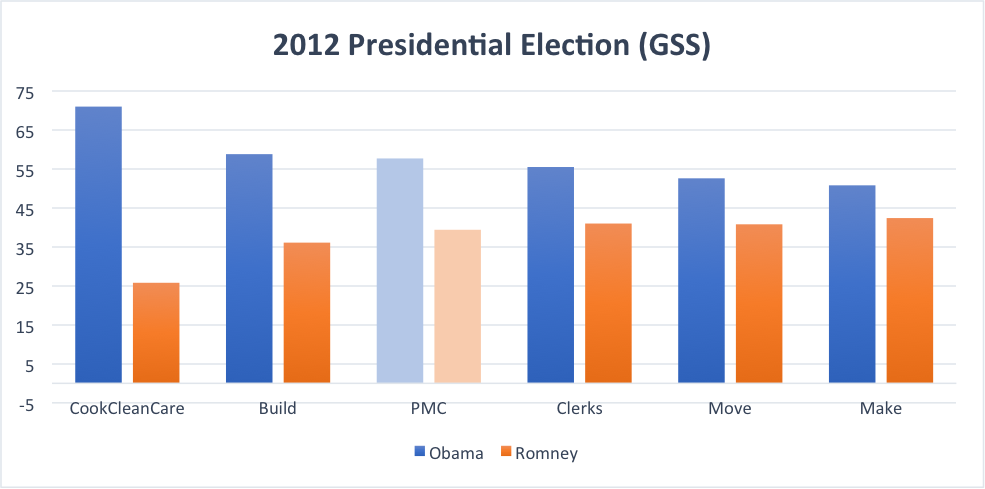
Organizing the data by job categories also helps us understand that white working-class men don’t vote as a unified bloc. If we look only at white men, Obama’s lead lessens, with Romney winning slight majorities with Makers, Movers, and Clerks (not to mention lots of PMC support). Why were white male Movers, Makers, and Clerks swayed by Romney while white male Builders and CookCleanCare were not? For one thing, the Democratic Party may have forgotten Movers and Makers. Women and people of color in these fractions may find other aspects of the Democratic party compelling, but white males less so. All five fractions took an economic hit during the Recession and, unlike the PMC, none of them have recovered, as you can see from the chart below. Makers even saw their wages decline before the recession hit.
Continue reading Looking at Fractions within the Working Class




